In ALL cases, preparing for the Sentencing Hearing should start as soon as possible.
Why?
a) Depending on whether it’s a state or federal case, there may only be weeks (or months) after the guilty verdict.
b) Getting all medical records via the HIPPA release can take a long time as some physicians and hospitals have been busy, especially in the age of COVID-19. HIPAA-COMPLIANT AUTHORIZATION FOR THE RELEASE OF PATIENT INFORMATION PURSUANT TO 45 CFR 164.508.
c) Coordinating character references, expert witnesses, and documentation for their PSR all takes time.
d) Developing the PSR, along with recommendations for placement, takes time.
I- The Presentence Report is used by;
1st) Judges
To establish the length of the sentence, along with they have the option to make a placement request.
2nd) The BOP, For Use It For Facility Placement.
3rd) Probation: Use it during Supervised Release.
4th) It then becomes a permanent part of the defendant’s record.
5th) Lastly, for inmates, it’s referred to as the ‘Inmates Bible.’
II) Sentence Length Determined By The Court based on;
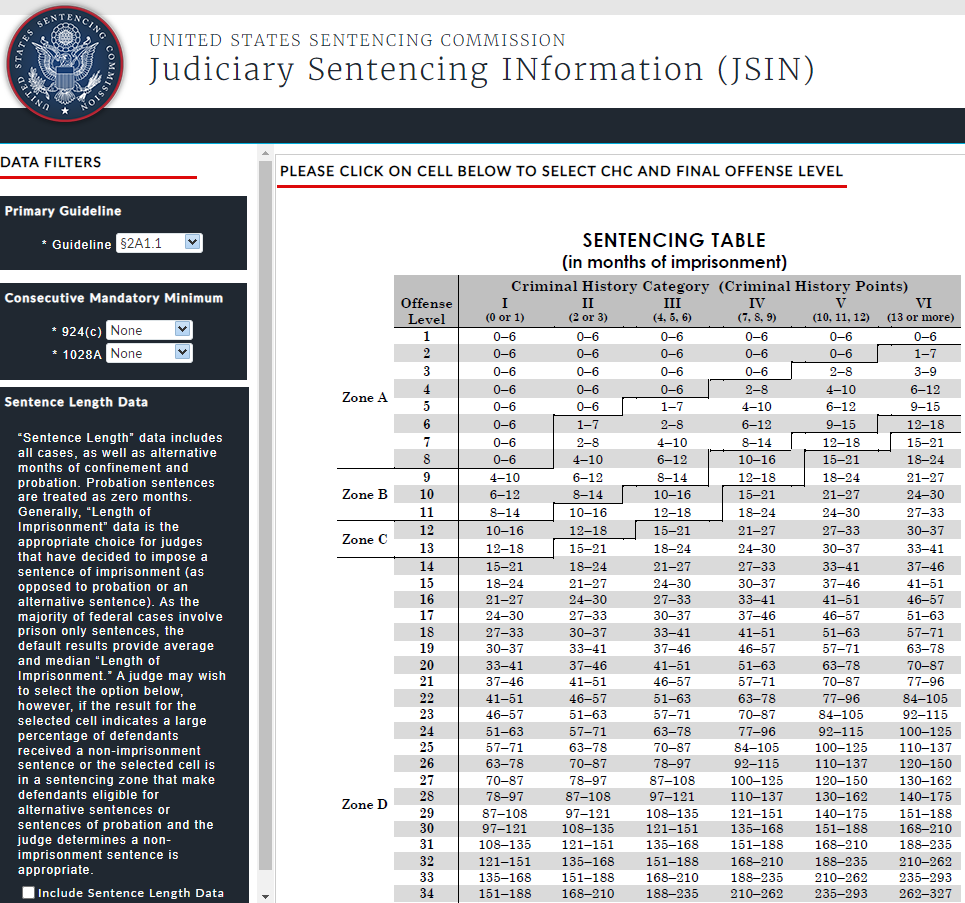
2021 (Released), Judiciary Sentencing INformation (JSIN) In real-time, the platform provides quick and easy online access to sentencing data for similarly situated defendants – An Updated USSC Sentencing Table.
USSC Sentencing Table (Point Based), [2018, CHAPTER 5: SENTENCING TABLE]
Offense Level (0-43+): *24+ categories.
Vs
Criminal History (0-13+)
Points for each prior sentence > 1 Year + 1 Month.
Points for each prior sentence > 60 days, not counted above.
Point for each prior sentence, <= 60 days not counted above, for up to a maximum of 4 points in this category.
Points for each revocation with a new charge or under federal supervision.
Point for each prior sentence resulting from a conviction of a crime of violence that did not receive any points as noted above because such sentence was treated as a single sentence, up to a total of 3 points for this subsection.
III) BOP Determines Placement Designation
1st) Healthcare: provided based on a CARE LEVEL I-IV Structure
Applies to Medical and Mental Healthcare CARE LEVELs.
Psychology and Life Skills National Programs have now been embedded into the First Step Act, with its limited availability and associated security requirements.
There are approximately 3,500 Medications in the BOP, which fall into 3 tiers. PPRS Prison Match™ has all of these drugs categorized by tier level should this apply to your client.
Is there a special diet request?
Allergies: all need to be documented in the PSR.
2nd) Non-Medical Placement is based on;
Bed Space Availability.
Aspirational: placement within 500 driving miles of legal residence.
Population Management: some inmates, for specified reasons, need to be monitored or separated from others.
2a) Public Safety Factors (PSF) & Management Variables [P5100.08, CN-I, 9/4/2019, Tables: Chapter 5, pages 12-13]
Could a Public Safety Factor (PSF: Chapter 4, pages 5-13) warrant a reduced security level?
Accepting Responsibility (may get point reductions).
Voluntary Surrender (gets point reductions).
Drug / Alcohol Abuse may allow RDAP.
RDAP; Required usage is within 1 year prior to the date arrested (illegal or legal medications or drugs).
AGE: 55+ (0Pts), 36-54 (2pts), 25-35 (4pts), <25 (8pts), Unknown (8pts).
Education Level: High School (0pts), GED Progress (1pt), No degree (2pts).
Sentence Length
>10 years – Low
>20 yrs – Medium, (Females: High)
>30 yrs – High
Disruptive Group
Male inmates will be housed in a High-security level institution unless the PSF has been waived.
Greatest Severity Offense
Males will be housed in at least a Low-security level institution unless the PSF has been waived.
Threat to Government Official
Male or female will be housed in at least a Low.
Deportable Alien: (male inmate who is not a citizen will be housed in at least a Low).
History Violent Behavior
A female inmate whose current term of confinement or history involves two convictions or findings – Low.
Serious Escape
A female, serious escape with the last 10 yrs. designated to Carswell Adm. Unit unless the PSF has been waived.
A male inmate with or without the threat of violence or escapes housed in at least a Medium.
Juvenile Violence
A male or female who has any documented:
a) Violent behavior, past or present, which resulted in a conviction, delinquency adjudication, or finding of guilt.
b) Violence: aggressive behavior causing bodily harm, death, or behavior likely to cause serious bodily harm.
Serious Phone Abuse
a) A male or female who utilizes the telephone to further criminal activities or Promote Illicit Organizations.
b) Conviction is Not Required, housed at least in a Low.
c) The PSF should be entered regarding any one of the following, if applicable.
Criminal acts conducted by telephone
-Leader/Organizer or primary motivator; or
a) communicate threats of bodily injury, death, assaults, or homicides.
b) conducts Fraudulent activity (actual or attempted) in an institution.
-Leader / Organizer who used the telephone to conduct fraudulent activity (actual or attempted)…
a) Smuggled narcotics or alcohol into a prison.
-Federal Law Enforcement notifies the BOP of concern and needs to monitor an inmate’s telephone calls…
a) The inmate has been found guilty of a 100 or 200-level offense code for telephone abuse.
b) A Bureau of Prisons official has reasonable suspicion and/or documented intelligence supporting telephone abuse.
Prison Disturbance
A male or female inmate who was involved in a serious incident of violence, Engaging / Encouraging a Riot:
a) Males will be housed in at least a HIGH-security level institution and
b) Females will be assigned to the Carswell Adm. Unit.

2b) Plus
a) Judicial Recommendations
b) Options For Work Cadre Participation (at secure facilities without satellite camps), where the inmate is allowed to work outside the perimeter of the institution.
c) PSF Waved: An inmate may receive up to three Public Safety Factors (PSFs) wavers.
d) Long Term Detainee transfers for positive or negative behavior may cause placement in a facility different from the scored security or custody level.
IV) Making The Placement Request
In recommending a facility placement, it’s helpful to provide a reason, for example:
To facilitate regular family visitation, or
To permit participation in a specific:
a) Medical CARE LEVEL
b) Mental Healthcare CARE LEVEL
c) Psychology has limited in availability and has associated security requirements.
d) Vocational Training Program
e) UNICOR job availability
V) Military: Is your client a Veteran?
If possible, connect your client with a facility that caters to veterans.
FCI Morgantown started a Veterans to Veterans Service Dog Training Program in 2016.
The Participants are federally imprisoned military veterans housed in a special wing responsible for training service guide dogs for veterans with mobility impairments, Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), or other military service missions.
If you’d like to discuss this, I look forward to speaking with you.
Dr. Blatstein
Physician Presentence Report Service
info@PPRSUS.com, 240.888.7778





 pleasure.
pleasure.